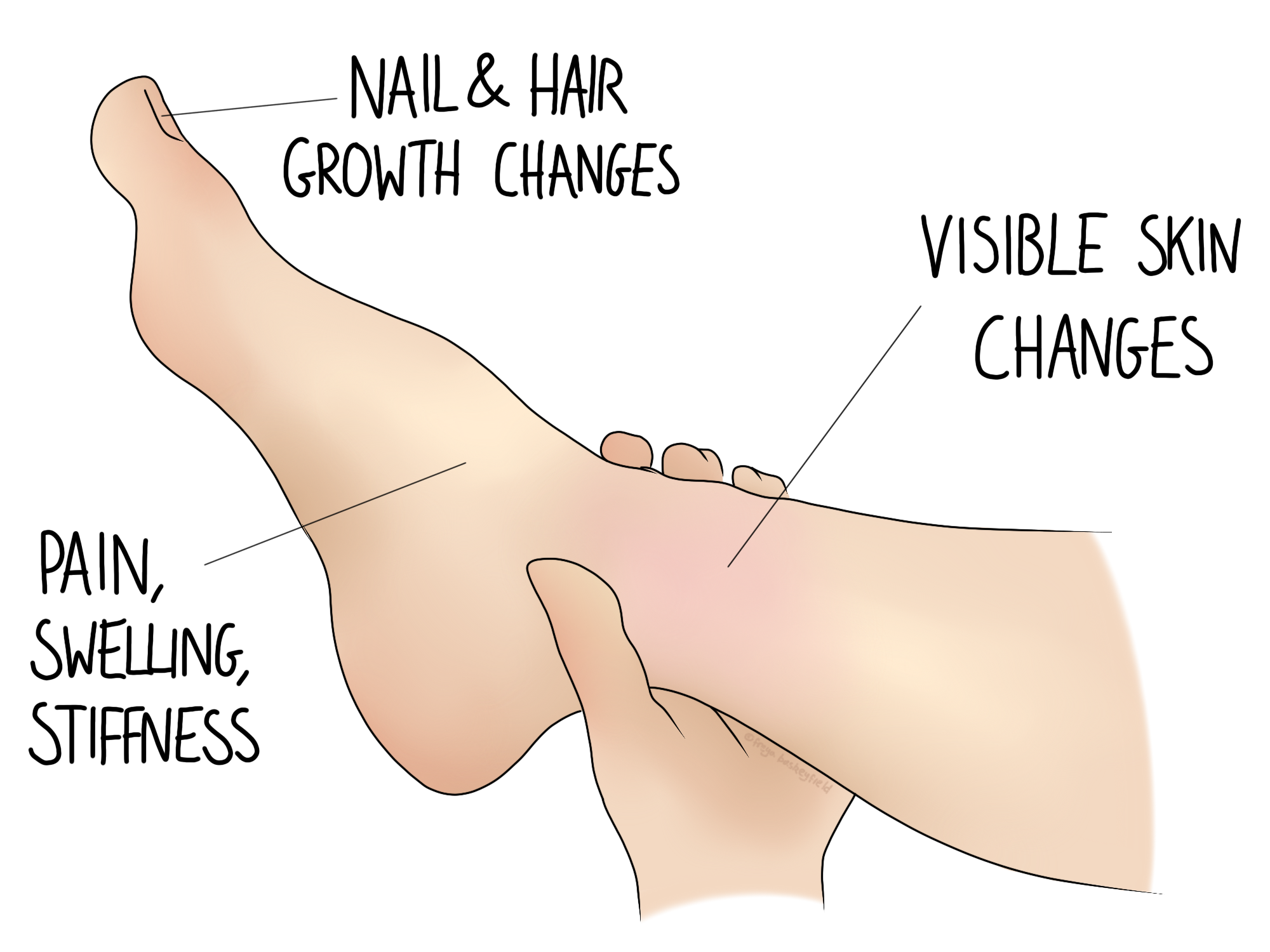
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) is a chronic pain condition that typically affects the limbs, often after an injury or surgery. This perplexing disorder is characterized by prolonged or excessive pain, changes in skin color, temperature, and swelling in the affected area. Despite extensive research, the exact cause of CRPS remains unclear, making it a challenging condition to diagnose and treat. This article delves into the intricacies of CRPS, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
What is CRPS?
CRPS, also known as Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy (RSD), is a rare but severe condition where the pain is out of proportion to the initial injury. It primarily affects one of the limbs—arms, legs, hands, or feet—after a trauma or surgery. CRPS is divided into two types:
- CRPS Type I: Previously known as RSD, this type occurs without a confirmed nerve injury.
- CRPS Type II: Formerly called causalgia, this type follows a distinct nerve injury.
While both types share similar symptoms, Type II has a more defined cause linked to nerve damage.
Causes of CRPS
The exact cause of CRPS is still under investigation, but it is generally believed to involve a combination of factors:
- Nerve Damage: CRPS is often triggered by an injury or surgery that damages the peripheral nerves, leading to an abnormal response from the nervous system.
- Immune System Response: Some researchers suggest that an abnormal immune response may play a role, causing inflammation that leads to the characteristic symptoms of CRPS.
- Sympathetic Nervous System Dysfunction: The sympathetic nervous system, which controls the body’s fight-or-flight response, may become overly reactive in people with CRPS, leading to persistent pain and other symptoms.
- Genetic Factors: There is some evidence to suggest that genetic predisposition may increase the risk of developing CRPS, although more research is needed to confirm this.
Symptoms of CRPS
The symptoms of CRPS can vary widely in intensity and duration but generally include:
- Chronic Pain: The most prominent symptom is intense, burning pain that is disproportionate to the initial injury. This pain can spread from the initial site to other areas of the limb or even to the opposite limb.
- Swelling: The affected limb may swell, sometimes significantly, causing stiffness and reduced mobility.
- Skin Changes: The skin in the affected area may undergo various changes, including:
- Color Changes: The skin may appear blotchy, pale, red, or even blue.
- Temperature Changes: The affected limb might feel unusually hot or cold compared to the other limb.
- Texture Changes: The skin may become thin, shiny, and sweaty, or it may thicken and become rough.
- Motor Dysfunction: People with CRPS often experience muscle weakness, tremors, and difficulty moving the affected limb. In severe cases, the limb may become rigid or fixed in a particular position (dystonia).
- Sensitivity: The affected area may become extremely sensitive to touch, a condition known as allodynia, where even light contact can provoke severe pain.
- Bone and Muscle Changes: Over time, CRPS can lead to bone loss (osteoporosis) and muscle wasting (atrophy) in the affected limb.
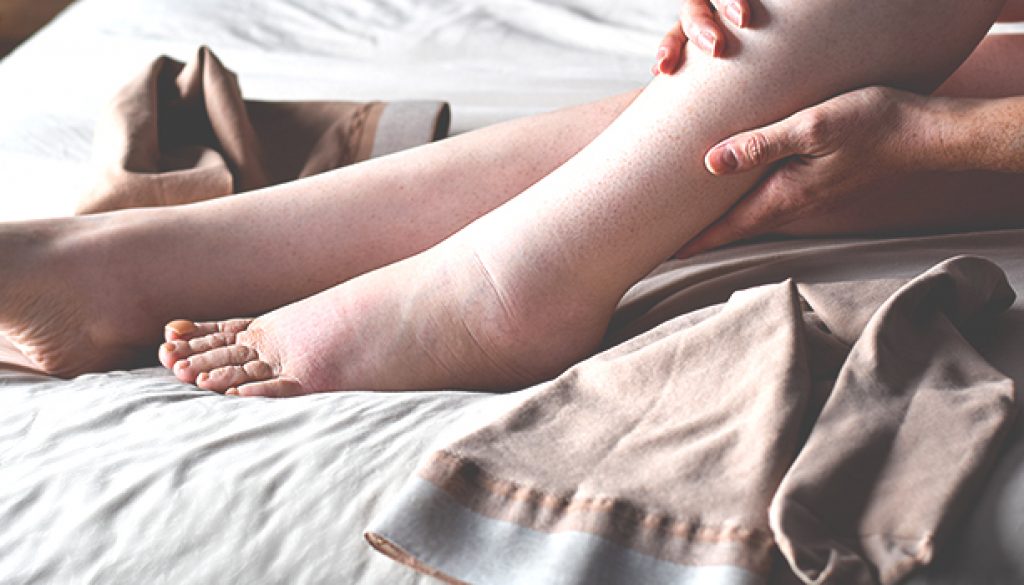

Diagnosis of CRPS
Diagnosing CRPS is notoriously difficult because its symptoms can mimic other conditions, and there is no single test to confirm it. Physicians usually rely on a combination of clinical evaluation, patient history, and diagnostic tests to rule out other causes of the symptoms. Common methods used in diagnosing CRPS include:
- Physical Examination: A thorough examination of the affected limb to check for signs of pain, swelling, color changes, and temperature differences.
- Bone Scans: These can reveal changes in bone metabolism that are often associated with CRPS.
- X-rays: In later stages of CRPS, X-rays may show bone loss or other changes.
- MRI: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) can detect tissue changes that may indicate CRPS.
- Sympathetic Nervous System Tests: These tests assess the function of the sympathetic nervous system, which may be involved in CRPS.
Treatment of CRPS
The treatment of CRPS is most effective when started early. It typically involves a multidisciplinary approach, combining various therapies to alleviate pain and improve function. Treatment options include:
- Medications:
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain medications, such as ibuprofen or aspirin, may help in the early stages. Stronger prescription medications, such as opioids, may be necessary for severe pain.
- Corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory drugs can reduce swelling and improve mobility in the affected limb.
- Antidepressants and Anticonvulsants: Medications like amitriptyline or gabapentin can be effective in managing nerve pain.
- Bisphosphonates: Drugs typically used to treat osteoporosis may help reduce bone pain and prevent bone loss in CRPS patients.
- Physical Therapy:
- Movement Therapy: Gentle, guided exercises can help maintain mobility and prevent stiffness in the affected limb.
- Desensitization Therapy: This involves exposing the affected area to different textures to reduce sensitivity and pain.
- Nerve Blocks:
- Sympathetic Nerve Blocks: These injections target the sympathetic nerves to relieve pain and improve blood flow to the affected area.
- Spinal Cord Stimulation:
- Implantable Devices: A device implanted near the spinal cord delivers electrical impulses that can mask pain signals.
- Psychological Support:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Chronic pain can have a significant impact on mental health. CBT can help patients develop coping strategies and improve their quality of life.
- Alternative Therapies:
- Acupuncture: Some patients find relief through acupuncture, which involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body.
- Biofeedback: This technique teaches patients to control certain physiological functions, such as heart rate and muscle tension, which can help reduce pain.
Living with CRPS
Living with CRPS can be challenging due to the persistent and often debilitating pain it causes. However, with early diagnosis and a comprehensive treatment plan, many people with CRPS can manage their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives. Support from healthcare professionals, family, and support groups is crucial in helping patients cope with the physical and emotional impact of the condition.
Conclusion
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) is a painful and perplexing condition that can significantly affect a person’s quality of life. Although the exact cause remains elusive, ongoing research continues to shed light on potential mechanisms and treatments. Early diagnosis and a multidisciplinary approach to treatment are key to managing CRPS and minimizing its long-term impact. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of CRPS, it is important to seek medical attention promptly to explore the available treatment options and begin the journey toward recovery.